Discovering How Omega-3 Fatty Acids Play a Vital Role in Inflammation Management
Understanding the Essential Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are indispensable lipids that are crucial for a multitude of physiological functions and processes within the human body. Notably, humans cannot synthesise these vital fats on their own, emphasizing the importance of obtaining them through dietary sources or supplements. The three primary types of omega-3 fatty acids include ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). Each type contributes uniquely to overall wellness, especially in terms of reducing inflammation and promoting cognitive health. As we explore ways to maximise omega-3 consumption for effective inflammation control, understanding their critical functions is essential.
Numerous research studies have consistently illustrated the extensive influence of omega-3 fatty acids on overall health and wellness. These beneficial fats are recognised for encouraging cardiovascular health by lowering triglyceride levels, regulating blood pressure, and improving vascular function. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids are vital for maintaining optimal brain function, positively affecting mood and cognitive capabilities. When consumed in adequate amounts, omega-3s can lead to significant improvements in health outcomes, underscoring their essential role in dietary guidelines worldwide.
Would you prefer to listen? Click below.
Investigating the Profound Impact of Inflammation on Overall Health
Inflammation serves as a natural biological response designed to protect the body from injury and infection. Acute inflammation is characterised by symptoms such as redness, swelling, and pain, all of which are crucial for the healing process. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to a host of health complications, including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. The link between chronic inflammation and the progression of various diseases underscores the need to address this issue through dietary changes, particularly by increasing the intake of omega-3 fatty acids.
Chronic inflammation often stems from lifestyle choices, such as poor dietary habits, lack of physical activity, and high stress levels. As we investigate the enhancement of omega-3 intake to counteract inflammation, it is clear that including sufficient amounts of omega-3s can help reduce the harmful effects of chronic inflammation. This significance is heightened by the rising incidence of inflammatory diseases globally. By prioritising inflammation reduction through dietary shifts, individuals can greatly improve their long-term health outcomes.
Unpacking the Mechanism of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Reducing Inflammation
Extensive research has shown that omega-3 fatty acids exhibit potent anti-inflammatory properties, effectively lowering the levels of inflammatory markers in the body. They achieve this by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines and eicosanoids, which helps to decrease the inflammatory response. This mechanism is particularly beneficial for those suffering from chronic conditions like arthritis, where inflammation is a key symptom.
The rationale behind enhancing omega-3 intake for inflammation management is supported by a substantial body of evidence. Numerous studies indicate that individuals with higher omega-3 levels in their bodies show reduced levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a well-known inflammation marker. This finding highlights the potential of omega-3 fatty acids to lower the risk of inflammatory diseases and improve overall health. Embracing dietary habits rich in omega-3s could provide significant public health benefits, especially in areas with high rates of inflammatory diseases.
Recognising Nutrient-Dense Foods High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids

Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your dietary routine can be achieved through a variety of nutrient-dense sources. Fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, rank among the richest sources of EPA and DHA. For those seeking plant-based alternatives, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are excellent sources of ALA, which the body can convert into EPA and DHA, though the conversion efficiency is lower.
The food industry has responded to the increasing demand for omega-3 fatty acids by fortifying a wide range of products. Certain eggs, dairy items, and even juices are now enhanced with omega-3s, allowing consumers to easily increase their intake. Algal oil, sourced from algae, presents another remarkable vegan option for acquiring EPA and DHA. This environmentally sustainable alternative to fish oil is becoming increasingly popular, especially among consumers who are conscious of their environmental impact.
Krill oil, derived from tiny crustaceans, is another viable source of omega-3 fatty acids, often considered more bioavailable than conventional fish oil. This means that the body can absorb and utilise the omega-3s present in krill oil more efficiently. When considering options for optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation, it is essential to select sources that align with your dietary preferences and requirements.
Exploring the Extensive Health Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Inflammation Management
Regular consumption of omega-3 fatty acids can yield a wide array of health benefits, particularly for individuals dealing with inflammatory conditions. Research indicates that people who maintain higher omega-3 levels in their diets experience reduced symptoms of arthritis and various inflammatory diseases, ultimately enhancing their quality of life. Omega-3 fatty acids are also associated with improved cardiovascular health, enhanced cognitive abilities, and better mood stability.
The benefits of omega-3 fatty acids extend beyond mere inflammation control. They play a crucial role in supporting cognitive health, with studies suggesting that adequate omega-3 intake may lower the risk of cognitive decline and mental health issues. By understanding the comprehensive advantages of omega-3s, individuals can make informed dietary choices that prioritise their overall health and well-being. As we investigate strategies for maximising omega-3 intake for inflammation management, it is essential to consider both the quantity and quality of omega-3 sources in one's diet.
Detailed Recommendations for Optimal Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake
Setting the Standard for Daily Omega-3 Consumption
Determining the appropriate dosage of omega-3 fatty acids requires adherence to general guidelines that advocate for a daily intake of 250-500 mg of combined EPA and DHA for adults. This benchmark is widely endorsed by health authorities and serves as a foundational guideline for maintaining overall health. Nevertheless, individual needs may vary based on lifestyle factors and specific health conditions, making it crucial to closely evaluate personal requirements.
For instance, individuals with active lifestyles or those experiencing heightened levels of inflammation may benefit from higher dosages. As we delve into the intricacies of optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation management, we must consider factors such as age, body weight, and overall health status. Consulting healthcare professionals can help ensure that you meet your specific omega-3 needs effectively.
Adopting a balanced approach to omega-3 consumption can significantly impact health outcomes. Regular intake of omega-3s not only addresses inflammation but also supports vital bodily functions, including cardiovascular health and cognitive performance. By staying informed about recommended dosages, individuals can proactively enhance their overall health and well-being.
Adjusting Omega-3 Dosage Based on Specific Health Conditions
Some medical conditions may require adjustments in omega-3 dosages. For example, individuals diagnosed with heart disease may benefit from increased intake, often ranging from 1,000 to 4,000 mg per day, as advised by healthcare providers. Likewise, those with rheumatoid arthritis or other inflammatory disorders may find that enhancing their omega-3 intake can significantly reduce inflammation and associated symptoms.
When aiming to optimise omega-3 intake for inflammation, it is crucial to work with a healthcare professional, especially when considering higher doses. This is particularly important for individuals currently taking medications for chronic conditions, as potential interactions may arise. Tailoring omega-3 intake to meet individual health needs can enhance effectiveness and improve health outcomes.
Individuals may also consider monitoring their omega-3 levels through blood tests to ensure they remain within optimal ranges. This approach allows for adjustments based on personal health goals and responses to supplementation, resulting in a more customised and effective health strategy.
Comparing Omega-3 Supplements with Dietary Sources
While ideally obtaining omega-3 fatty acids from food should be the primary method of consumption, supplements offer a practical alternative for those unable to achieve their needs through diet alone. Fish oil capsules, krill oil, and algal oil are popular supplement forms that provide concentrated doses of omega-3s.
However, prioritising quality when selecting omega-3 supplements is essential. Opt for products that have undergone third-party testing for purity and potency, ensuring they are free from harmful contaminants. While supplements can be beneficial, they should not replace a balanced diet rich in whole foods. Emphasising a nutrient-dense diet enhances overall health and aligns with the goal of optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation management.
Incorporating foods rich in omega-3s into one’s diet represents a sustainable approach that not only aids in managing inflammation but also contributes to overall well-being. By prioritising dietary sources, individuals can benefit from additional vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals found in whole foods, thereby enhancing their health on multiple levels.
Highlighting Nutrient-Rich Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Emphasising Fatty Fish as a Primary Source of Omega-3s
Fatty fish are among the most abundant sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA. Species such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies are rich in these essential fats. It is generally recommended to consume fatty fish at least twice a week to effortlessly meet omega-3 requirements.
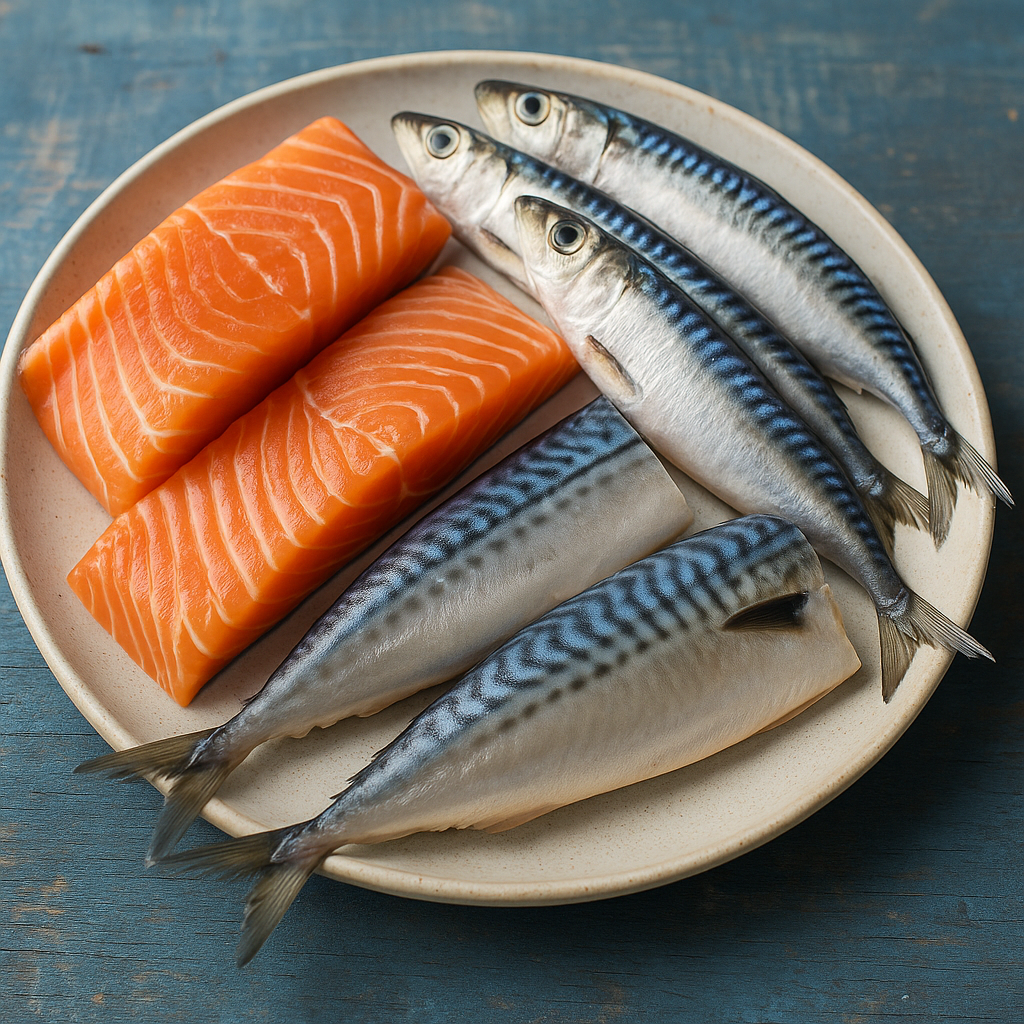

In addition to their omega-3 content, these fish are also abundant in high-quality protein, vitamins, and minerals, making them a cornerstone of a nutritious diet. Regular consumption of fatty fish offers numerous health benefits, including reduced inflammation, enhanced heart health, and improved cognitive function. As we explore methods to optimise omega-3 intake for inflammation, incorporating fatty fish into your meals can significantly contribute to achieving desired health outcomes.
For those with dietary restrictions or preferences that limit fish consumption, alternatives are readily available. Canned fish, such as sardines and tuna, provide convenient options that preserve their nutritional integrity. Cooking methods like grilling, baking, or even smoking fish can add variety to meals, ensuring that individuals can enjoy the health benefits of omega-3s without falling into a routine.
Examining Plant-Based Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
For individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets, there are numerous plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids available. Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are exceptional sources of ALA, the plant-derived omega-3. While ALA must be converted into EPA and DHA within the body, it still offers significant anti-inflammatory benefits.
Incorporating these nutrient-rich foods into your diet can be straightforward, such as adding flaxseeds to smoothies or oatmeal, sprinkling chia seeds on salads, or snacking on a handful of walnuts. Focusing on plant-based omega-3 sources aligns seamlessly with the goal of optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation, particularly for those embracing vegetarian or vegan lifestyles.
Moreover, other foods such as edamame, seaweed, and certain green leafy vegetables also contain ALA and can contribute to overall omega-3 intake. Incorporating a variety of sources ensures a balanced approach to omega-3 consumption, catering to diverse dietary preferences and needs.
Investigating Omega-3 Fortified Foods for Increased Intake
In recent years, the food industry has adapted to the growing demand for omega-3 fatty acids by fortifying a diverse range of products. Foods such as specific eggs, dairy products, and even orange juice are now enriched with omega-3 fatty acids, presenting individuals with a straightforward way to boost their intake, especially if they find it challenging to consume sufficient omega-3-rich foods.
Fortified foods can be particularly advantageous for those who may not enjoy fish or plant-based omega-3 sources. As we consider optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation, incorporating these fortified foods could provide a practical solution for enhancing overall omega-3 consumption. However, it is essential to scrutinise product labels to ensure that these items contain beneficial levels of omega-3s.
While fortified foods can supplement a diet lacking omega-3s, they should not completely replace whole food sources. A multifaceted approach that includes natural sources alongside fortified options can yield comprehensive health benefits.
Understanding the Benefits of Algal Oil as a Sustainable Vegan Source
Algal oil, derived from algae, serves as a sustainable and vegan source of EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids. This oil is gaining popularity, particularly among those concerned about the environmental impacts of traditional fish farming and fishing practices. By utilising algae, we gain access to a rich source of omega-3s without depleting ocean resources.
The advantages of algal oil extend beyond sustainability, as it provides omega-3s in a form that the body readily absorbs, comparable to fish oil. As we explore strategies for optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation, algal oil stands out as an appealing option for those looking to increase their intake of these essential fatty acids while adhering to plant-based diets.
Regular consumption of algal oil can be especially beneficial for individuals at risk of inflammatory conditions. Research suggests that algal oil supplements may aid in reducing inflammatory markers and promoting overall health. As this option continues to gain traction, it offers an exciting opportunity to enhance global omega-3 intake.
Investigating the Benefits of Krill Oil for Omega-3 Consumption
Krill oil, sourced from small Antarctic crustaceans, represents another highly bioavailable source of omega-3 fatty acids. It contains both EPA and DHA and is often praised for its superior absorption characteristics compared to traditional fish oil. The phospholipid form of omega-3s found in krill oil enhances absorption, making it an attractive choice for those seeking to effectively boost their omega-3 intake.
In addition to omega-3s, krill oil is also rich in antioxidants, particularly astaxanthin, which adds further health benefits. Research indicates that krill oil may bolster heart health, diminish inflammation, and enhance cognitive function. When contemplating the optimisation of omega-3 intake for inflammation, krill oil can serve as a significant ally in fostering overall wellness.
Despite its numerous benefits, caution should be exercised when considering krill oil supplementation. Individuals with shellfish allergies should avoid it, and consulting a healthcare professional is recommended before starting any new supplementation regimen. Emphasising a variety of omega-3 sources, including krill oil, can provide a well-rounded strategy for enhancing global health.
Recognising Possible Side Effects and Important Precautions
Identifying Common Side Effects Associated with Omega-3 Supplementation
While omega-3 fatty acids are generally considered safe, high doses may lead to mild side effects. Individuals might experience a fishy aftertaste, nausea, or loose stools, especially when introducing omega-3 supplements into their routine. These side effects can typically be mitigated by taking supplements with meals or by choosing enteric-coated capsules designed to minimise the fishy taste.
When optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation, it is crucial to adhere to recommended dosages. Surpassing these guidelines can result in more severe side effects, such as an increased bleeding risk or gastrointestinal issues. For most individuals, moderate supplementation effectively manages inflammation without significant adverse effects.
If side effects persist, individuals should reassess their omega-3 intake and consult a healthcare provider. By ensuring that omega-3 consumption remains within safe limits, individuals can reap the extensive benefits of these essential fatty acids while minimising discomfort risks.
Understanding Interactions Between Omega-3s and Medications
Omega-3 supplements may interact with specific medications, particularly blood thinners like warfarin and aspirin. Given that omega-3s have blood-thinning properties, excessive consumption could heighten the risk of bleeding, especially during surgeries or when combined with anticoagulant medications.
When considering the optimisation of omega-3 intake for inflammation, individuals on medication must consult their healthcare provider before initiating or significantly increasing their omega-3 consumption. This proactive approach ensures safe and effective management of inflammation while minimising the potential for adverse interactions.
Regular monitoring and open dialogue with healthcare professionals can facilitate the effective management of potential interactions. This proactive strategy allows individuals to safely benefit from omega-3s while managing their existing medical conditions.
Recognising Those Who Should Avoid Omega-3 Supplements
Certain individuals should exercise caution or completely avoid omega-3 supplements. Those with bleeding disorders or conditions that elevate bleeding risk should carefully evaluate their omega-3 intake. Additionally, individuals with allergies to fish or shellfish should refrain from consuming fish-based omega-3 supplements, opting instead for plant-derived alternatives such as flaxseed or algal oil.
As we delve into optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation, it is crucial to approach supplementation with a clear understanding of individual health conditions. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed choices prioritising their safety and health.
For those uncertain about their suitability for omega-3 supplementation, consulting with a healthcare professional can provide clarity and guidance. This personalised approach ensures that individuals can explore the potential benefits of omega-3s while addressing their unique health needs.
Practical Methods for Evaluating Omega-3 Levels
Utilising Blood Tests to Determine Omega-3 Index
Assessing omega-3 levels in the body can be effectively achieved through blood tests that measure the Omega-3 Index. This test evaluates the percentage of EPA and DHA in red blood cell membranes, offering essential insights into an individual’s omega-3 status. A higher Omega-3 Index is linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases, making this test a valuable tool for those looking to optimise their omega-3 intake.
Regular testing allows individuals to monitor the effectiveness of their dietary or supplemental omega-3 strategies. As we contemplate optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation, understanding one’s Omega-3 Index can provide valuable feedback for necessary adjustments. This approach fosters a personalised strategy to meet health objectives more effectively.
Healthcare professionals often recommend periodic testing, particularly for individuals with inflammatory conditions or those striving to maintain optimal health. By actively monitoring omega-3 levels, individuals can ensure they maximise the benefits of their dietary choices.
Interpreting Omega-3 Testing Results for Informed Decision-Making
An Omega-3 Index of 8% or higher is generally considered optimal for minimising inflammation and enhancing overall health. However, many individuals may fall below this threshold, highlighting the need to prioritise omega-3 intake. Understanding the implications of test results can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices that align with their health goals.
When interpreting results, it is crucial to consider contributing factors such as dietary habits, lifestyle choices, and overall health status. Individuals with lower Omega-3 Index levels may need to increase their consumption of omega-3-rich foods or consider supplementation to improve their health outcomes.
As we focus on optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation, interpreting test results provides a clear guideline for enhancement. By establishing personal targets based on the Omega-3 Index, individuals can progress towards a healthier, more balanced lifestyle that emphasises anti-inflammatory benefits.
The Importance of Routine Monitoring for Optimal Health
Regular monitoring of omega-3 levels is vital for maintaining optimal health and ensuring the effectiveness of dietary changes or supplementation. Tracking your omega-3 intake over time aids in identifying patterns in your levels, facilitating necessary adjustments to your diet or supplements as needed.
Many individuals may find it beneficial to set reminders for regular testing, especially if managing chronic inflammatory conditions. This proactive approach ensures that omega-3 intake aligns with health goals, allowing for timely modifications to optimise benefits.
Consistent monitoring plays a crucial role in any strategy aimed at enhancing health through optimising omega-3 dosages. It helps track progress and allows for necessary adjustments. Staying engaged with your health enables improved decision-making, ultimately enhancing daily well-being and minimising the impact of inflammation on your body and overall health.
Understanding Lifestyle Factors Influencing Omega-3 Effectiveness
Examining the Connection Between Diet and Omega-3 Efficacy
Your dietary choices can significantly affect the effectiveness of omega-3 fatty acids. A diet high in processed foods, sugars, and trans fats can undermine the benefits of omega-3s, potentially increasing inflammation instead of alleviating it. To fully harness the advantages of omega-3s, it is vital to adopt eating habits that enhance their effects. This involves selecting a balanced, nutritious diet that complements rather than detracts from their positive impacts.
Prioritising whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, enhances the body’s ability to utilise omega-3s effectively. This dietary framework not only supports the efficacy of omega-3s but also contributes to overall health and wellness. As you consider optimising your omega-3 intake for inflammation, it is crucial to recognise that the quality of your diet is as significant as the quantity of omega-3s consumed.
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, like <a href=”https://limitsofstrategy.com/turmeric-the-golden-spice-for-health-advantages/”>turmeric</a>, ginger, and various spices can further amplify the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids. The synergistic effects of these foods can assist the body in combating inflammation and promoting optimal health outcomes.
Integrating Regular Exercise to Enhance Omega-3 Benefits
Consistent physical activity acts as a powerful ally in maximising the benefits of omega-3s. Regular exercise can help reduce inflammation and enhance the body's ability to utilise omega-3 fatty acids effectively. Maintaining an active lifestyle can significantly improve overall health, including weight-bearing exercises and cardiovascular activities. Research indicates that individuals who engage in consistent exercise exhibit lower inflammatory markers in their bodies. This highlights the importance of combining physical activity with omega-3 intake to achieve optimal health outcomes.
As you strategise on optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation, consider integrating exercise into your routine as a complementary approach. Whether through walking, cycling, or strength training, discovering enjoyable ways to stay active can empower you to fully leverage the potential of omega-3s in your health journey.
Implementing Effective Stress Management Strategies for Enhanced Health
Chronic stress can elevate inflammation levels, underscoring the importance of effective stress management strategies. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on the body, creating an environment that is more conducive to omega-3 effectiveness.
 Incorporating stress management practices can enhance your overall health as you focus on optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation. By addressing the root causes of inflammation through a holistic approach, you empower your body to respond positively to dietary changes and supplementation.
Incorporating stress management practices can enhance your overall health as you focus on optimising omega-3 intake for inflammation. By addressing the root causes of inflammation through a holistic approach, you empower your body to respond positively to dietary changes and supplementation.
Engaging in regular self-care, prioritising quality sleep, and cultivating strong social connections can further enhance resilience against stress. This multifaceted strategy allows for a comprehensive approach to managing inflammation and promoting overall wellness.
Common Questions Regarding Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Benefits
What are omega-3 fatty acids and why are they essential for health?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that the body cannot produce independently. They are crucial for various health functions, including reducing inflammation, supporting heart health, and enhancing brain function.
How do omega-3s effectively combat inflammation?
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory molecules within the body, thereby alleviating chronic inflammation associated with various diseases.
What is the recommended daily intake of omega-3s for optimal health outcomes?
The general recommendation for adults is to consume 250-500 mg of combined EPA and DHA daily. However, individual needs may vary depending on health conditions and lifestyle choices.
Can I obtain sufficient omega-3 from a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Vegetarians can secure omega-3 fatty acids from plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, which provide ALA. However, the conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA is limited in the body.
Are omega-3 supplements considered safe for general use?
Omega-3 supplements are generally regarded as safe when consumed within recommended dosages. However, those on blood-thinning medications or with allergies should consult a healthcare provider before use.
How can I measure my omega-3 levels to ensure I am within a healthy range?
Omega-3 levels can be assessed through blood tests that evaluate the Omega-3 Index, indicating the percentage of EPA and DHA present in red blood cell membranes.
What foods are rich in omega-3 fatty acids?
Fatty fish such as salmon and sardines, along with plant-based sources like flaxseeds and walnuts, are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
What are the common side effects associated with omega-3 supplements?
Common side effects of omega-3 supplements may include a fishy aftertaste, nausea, and loose stools, particularly when taken at higher doses.
Can omega-3 fatty acids provide relief for arthritis symptoms?
Yes, omega-3 fatty acids can help alleviate arthritis symptoms by reducing inflammation and improving joint health and mobility.
Is krill oil considered superior to fish oil for omega-3 intake?
Krill oil is often regarded as more bioavailable than fish oil, facilitating better absorption of omega-3s. However, individual preferences and health requirements should guide supplement choices.
Connect with us on Facebook!
The Article: Omega-3s Fight Inflammation: Boosting Health Naturally appeared first on https://janestevensnutrition.com
The Article Omega-3s: Naturally Boost Health and Combat Inflammation Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com
The Article Omega-3s: Enhance Health and Fight Inflammation Naturally First Appeared ON
: https://ad4sc.com
No responses yet